Causes of Inflation and its Relationship with Foreign Exchange
Inflation (= meaning the generalized and continuous increase of prices in an economy) is a very important economic phenomenon, affecting practically all investments in financial assets in the capital market. Therefore, for investors and traders alike it is highly recommended to understand the dynamics of inflation and some of its causes. One of the causes that influences inflation is the level of economic activity. When an economy is heated, with very low unemployment and a sufficient demand pressure, prices tend to accelerate, causing inflation. This also occurs due to pressure for wage increases in the labor market, which causes companies to transfer these costs to the prices of their products and services. This increase in wages and prices, if strong, can therefore cause inflation.
A second cause of inflation can be exchange rate devaluation. With exchange/currency devaluation, imports become more expensive, and this can lead to an increase in prices in the domestic market for products that depend precisely on imports from abroad, reflecting on the entire economy. With exchange appreciation, in turn, inflation tends to fall. A third cause of inflation is considered to be supply shocks, representing an increase in the prices of important inputs (such as commodities), which tend to affect the entire economy as well, such as gasoline and petroleum-derived fuels. In any case, what are the main indicators of inflation in an economy? Usually these indicators involve the so-called 'consumer price indexes' which are collected by the statistics departments of each country.
In the FBS economic calendar, our traders can find some important indicators regarding inflation:
- In Switzerland, the most important categories of the Consumer Price Index involve: Housing and Energy (27% of the total weight), Health (18%), Food and Non-Alcoholic Beverages (12%) among others;
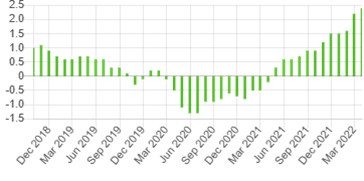
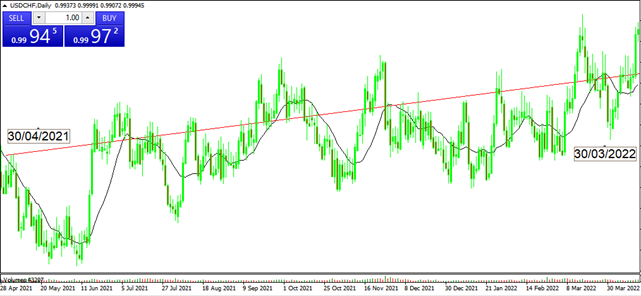
We see for example that the increase in the Swiss inflation rate between April 2021 (0.3%) and March 2022 (2.4%) appeared to have been (in part) a reflection of the devaluation of the franc (CHF) against its international peers, mainly the USD. In the chart below, we see the appreciation of the USD against the CHF in the period indicated.
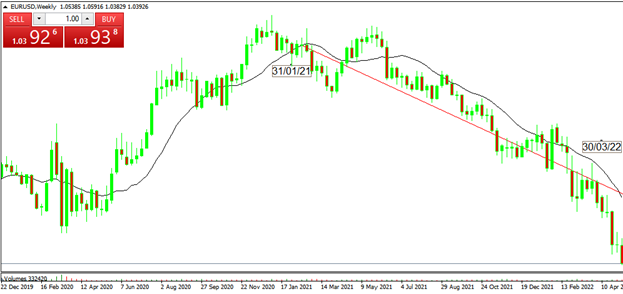
- In the Euro Zone, the Inflation Rate is calculated by the weighted average of the aggregates of the Harmonized Consumer Price Index for each country, whose main components are: Services (41%), Non-Energy Industrial Goods (29% of the total), Food, Alcohol and Tobacco (19%) and Energy (11%).
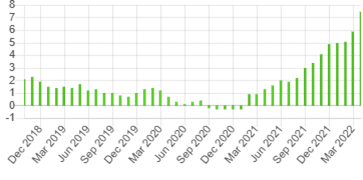
We see for example that the increase in the Eurozone inflation rate between January 2021 (0.9%) and March 2022 (7.5%) appeared to have been (in part) a reflection of the devaluation of the Euro (USD) against its international peers, especially the USD. In the chart below we see the devaluation of the EUR against the USD in the period indicated.