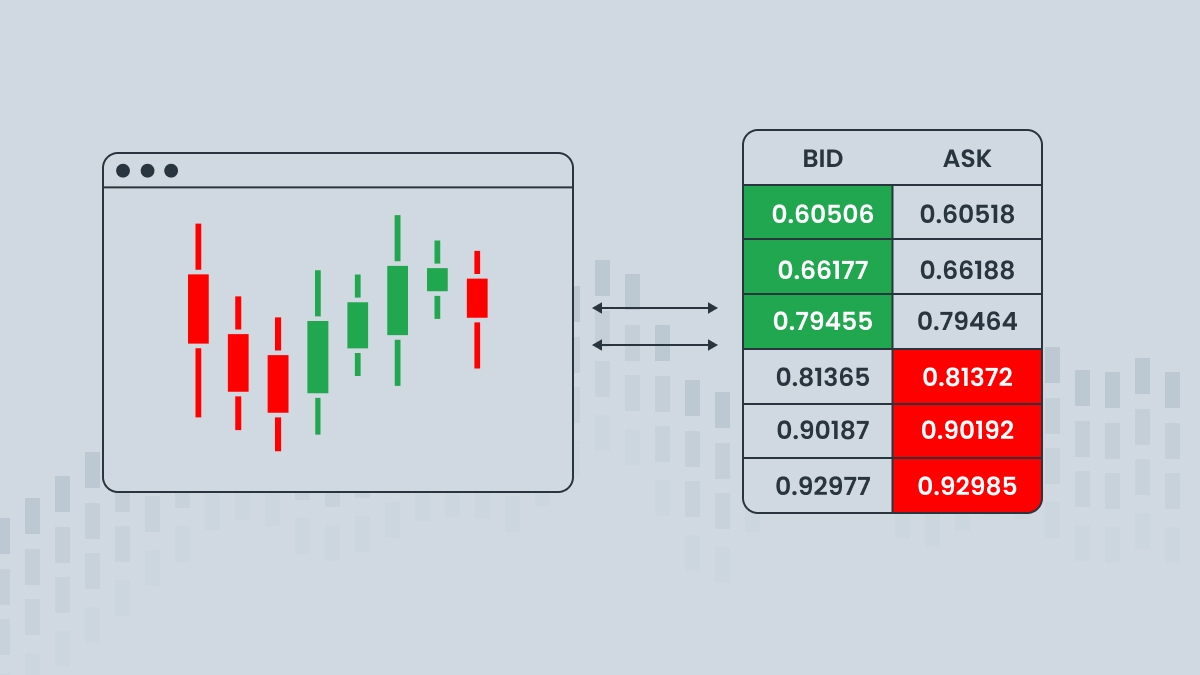
Order books are real-time snapshots of market demand, but they are also called “continuous” because they are updated in real time as soon as each order is placed and filled. In this way, it is kind of like watching a tug-of-war play out in real time. An exchange’s order book is not to be confused with a company’s order book, which is a log of its customer orders.
The highest bid and lowest ask prices are shown at the top, bottom, or sides, depending on the order book. They indicate the current market price and sometimes include candlestick charts that show how prices are and have been moving.
Types of orders
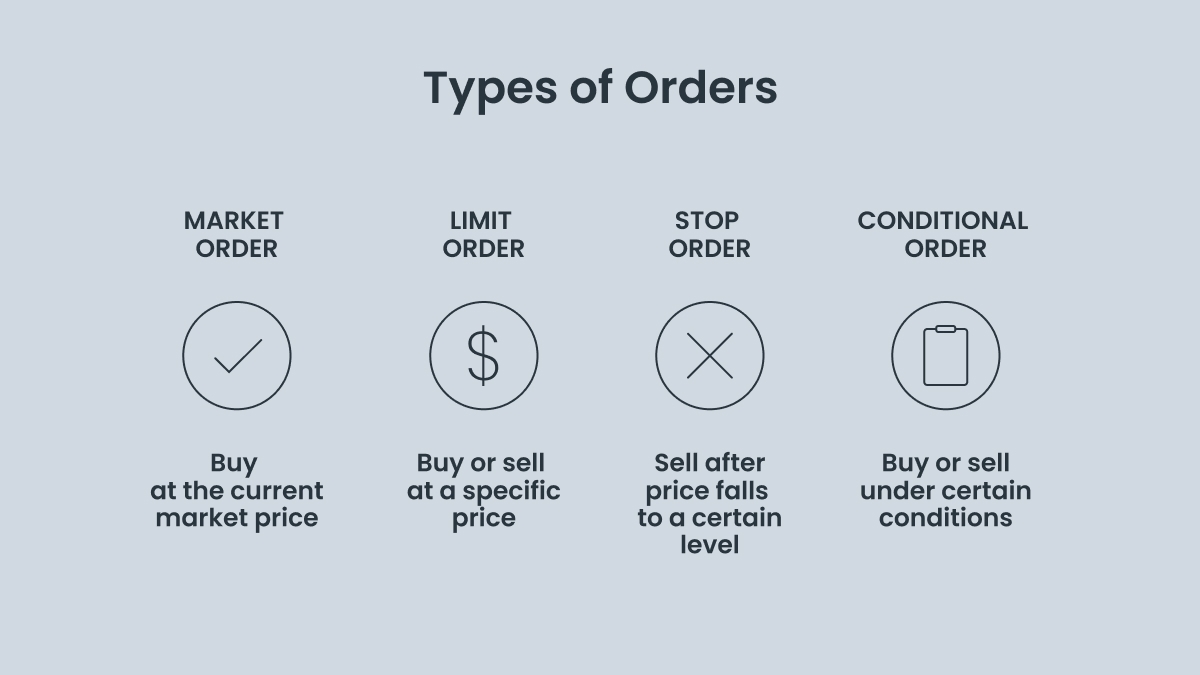
There are different types of buy and sell orders that traders can place depending on their trading strategy:
Market orders are placed by traders who want to buy stocks at the current market price. These orders are usually filled almost instantly. The price that traders see when they place the order is not necessarily the price it executes for when the market is volatile, so in this way, market orders prioritize execution speed over price.
Limit orders are when traders want to buy or sell shares at a specific price of their choosing. This price can be the market price, but it can also be higher when they feel that the market price is too cheap to sell, or lower when they feel that it’s too expensive to buy. These orders prioritize price over speed, and it can take a while before the limit price is actually reached, if it ever is. Sometimes the stock keeps moving in one direction and never reverses, and other times price movements are so volatile that the limit price is skipped and the order doesn’t get placed. Although this gives traders more control over price, there is no guarantee that their order will ever be filled.
Stop orders, or stop-losses, are used by traders who know that they want to sell a security after it falls below a certain price, to limit losses or secure some gain. This is useful when traders don’t have time to sit in front of the exchange and monitor prices in real time. They choose a limit price that will trigger a market order once that price level is breached. When the market is volatile, however, the execution price can be much lower than the stop-loss limit.
Other conditional orders can be placed by traders who only want their trades to be filled under certain specific conditions. An All-or-None (AON) order means that the trader does not want any partial fills. The order must be filled completely or not at all. Fill-or-Kill (FOK) means the trader wants the order to be filled immediately and in its entirety, or it is canceled. Immediate-or-Cancel (IOC) orders are the same as FOKs but with partial fills allowed. These more complex orders give traders increased control over how and when their trades are filled.