ESG Metrics
ESG metrics evaluate how well a company meets specific environmental, social, and governance criteria.
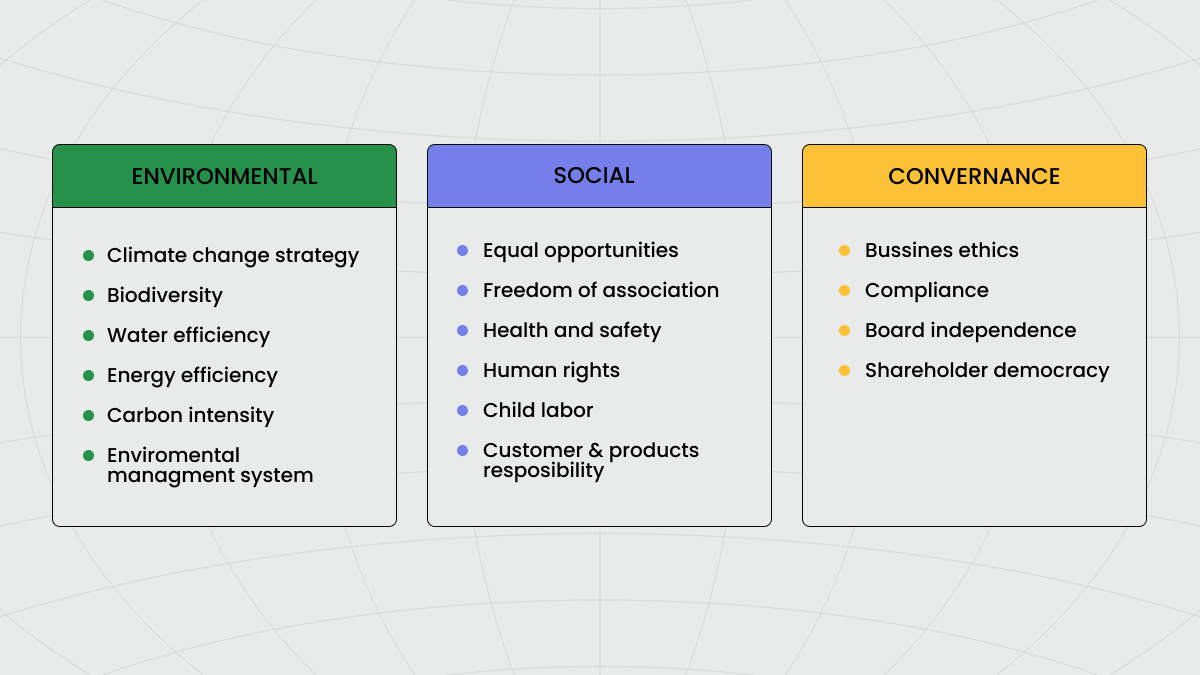
What ESG Criteria To Look At
Environmental criteriaThis group of metrics assesses how a company impacts the environment. Investors consider energy use, waste and carbon emissions, pollution and water usage, and treatment of animals. Additionally, investors pay attention to any environmental risks a company might face and how it will manage them. There are certain tools that score companies based on environmental transparency and actions. You can use the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) to understand these criteria.
Social criteriaThese metrics examine how a company handles its relations with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities in operation regions. These criteria evaluate factors related to human rights, labor practices, child labor, workplace and product safety, diversity and inclusion, community relations, data protection, and overall impact on society.
Governance criteriaIt is generally believed that good management practices can reduce corruption, improve a company’s reputation, and make it more sustainable in the long run. Investors evaluate a company’s leadership, executive pay, board diversity, accounting transparency, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
Sometimes, negative screening is used in ESG investing to exclude companies that don’t meet specific standards.
Investors and ESG
The growing interest in ESG investing reflects a shift in priorities. We see that both individual and institutional investors want to make their investment strategies more sustainable and ethical.
A major role in the growing popularity of ESG investing belongs to institutional investors: pension funds, insurance companies, investment funds, etc. They request better ESG disclosures because they want to understand all the factors that can affect the financial performance and risks of their investments.
Individual investors also pay attention to ESG factors. They want to align their portfolios with their ethical beliefs and still receive higher returns. Many retail investors prefer companies that prioritize sustainability, as they believe that such companies are better prepared for future challenges and will be more profitable over time.
The Difference between ESG Investing and Sustainable Investing
The terms ESG investing and sustainable investing are often used interchangeably. However, they are based on different ethical, environmental, and social guidelines to align investments with personal values and long-term financial goals.
ESG investing
This approach evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance factors. Traditional financial metrics are also considered when making decisions. This type of investment focuses on how these factors affect economic performance. A study also made of a company’s operations and risk management.
Sustainable investing
This approach is thought to be broader than ESG. It considers ESG criteria and targets investments in companies that produce positive environmental or social impact. These may be renewable energy projects or innovative companies in healthcare. Sustainable investing often uses positive screening to choose companies that contribute to social or environmental objectives.