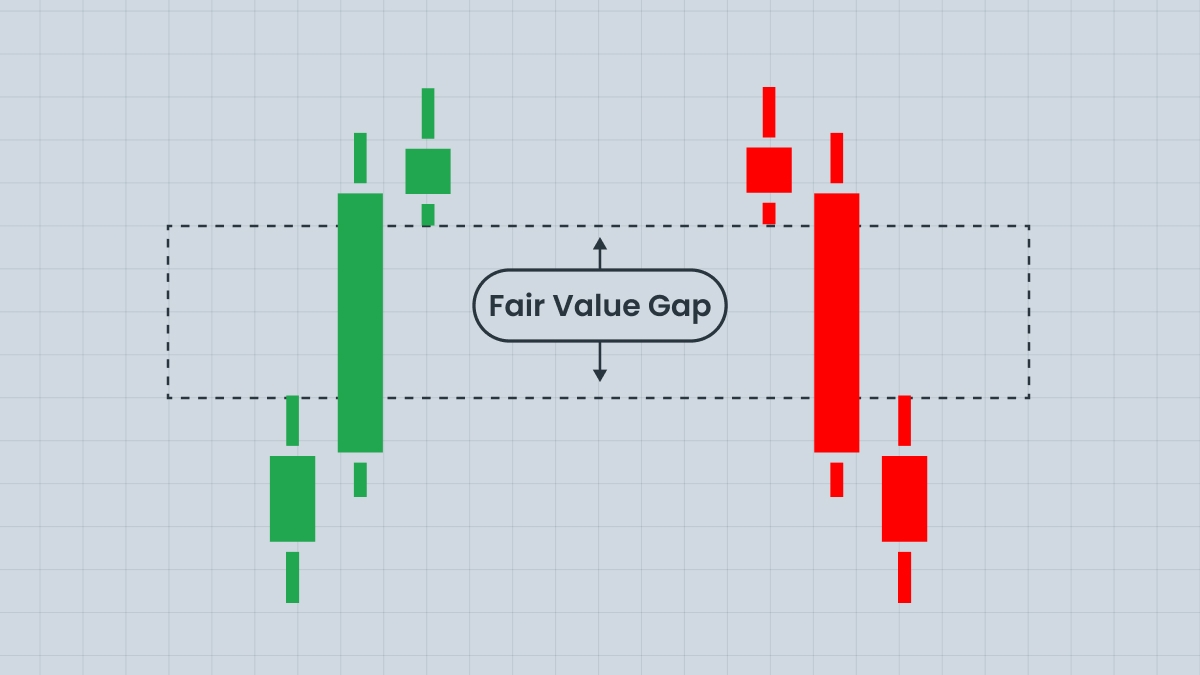
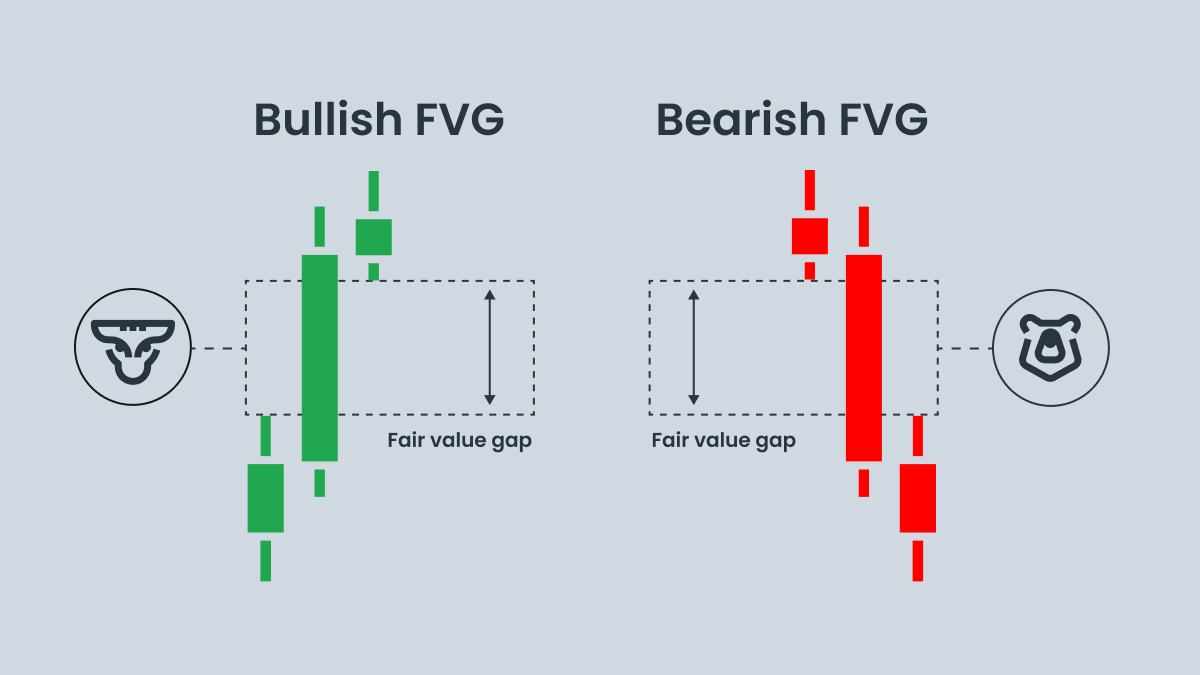
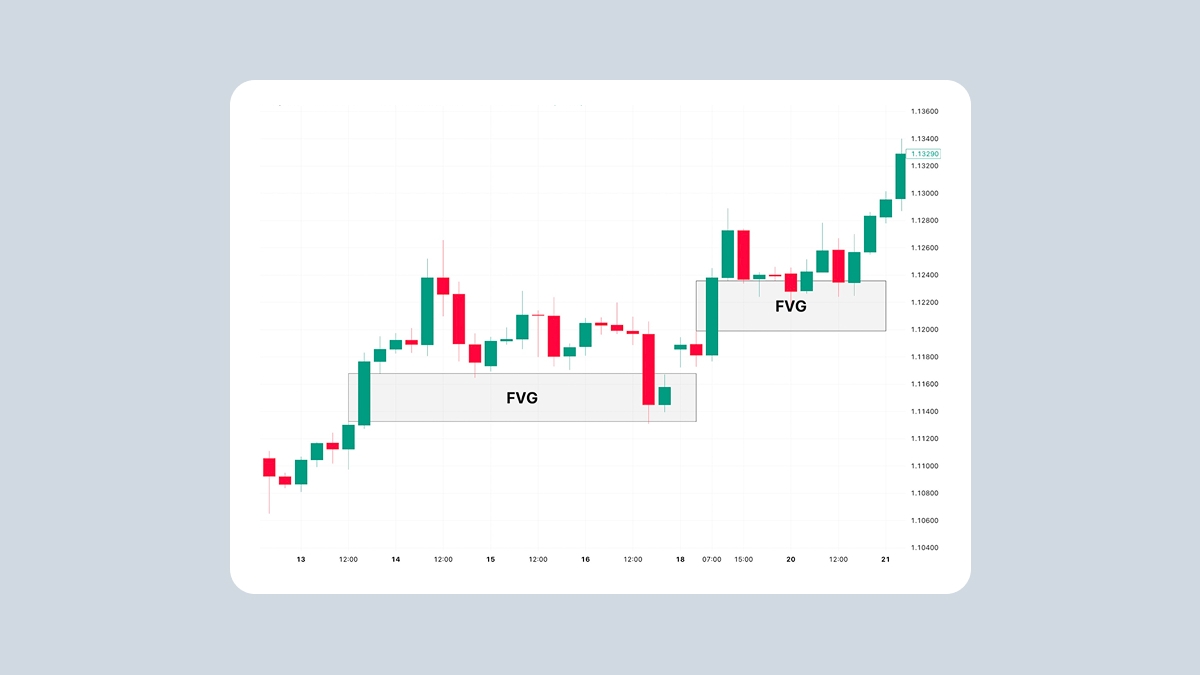
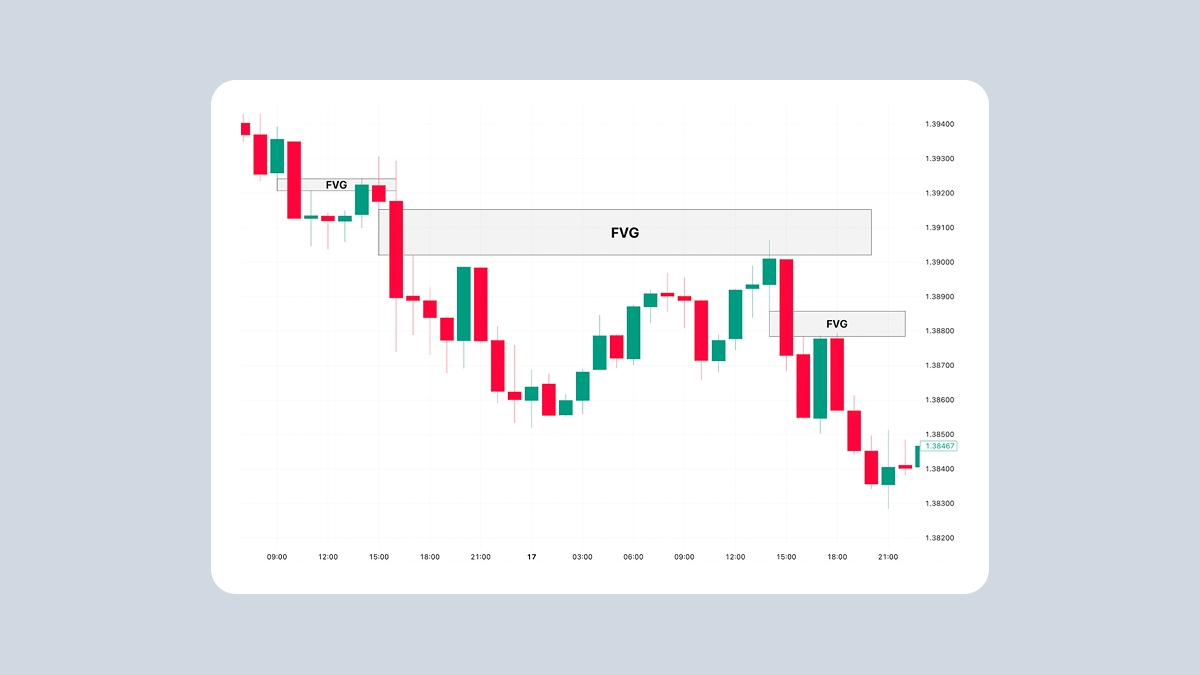
The website is operated by FBS Markets Inc.; Registration No. 000001317; FBS Markets Inc. is registered by the Financial Services Commission under the Securities Industry Act 2021, license number 000102/31. Office Address: The Bentley, #16 Cor A Street & Princess Margaret Drive, Belize City, Belize.
FBS Markets Inc. does not offer financial services to residents of certain jurisdictions, including, but not limited to: the USA, the EU, the UK, Israel, the Islamic Republic of Iran, Myanmar.
Payment transactions are managed by HDC Technologies Ltd.; Registration No. HE 370778; Legal address: Arch. Makariou III & Vyronos, P. Lordos Center, Block B, Office 203, Limassol, Cyprus. Additional address: Office 267, Irene Court, Corner Rigenas and 28th October street, Agia Triada, 3035, Limassol, Cyprus.
Contact number: +357 22 010970; additional number: +501 611 0594.
For cooperation, please contact us via [email protected].
Risk Warning: Before you start trading, you should completely understand the risks involved with the currency market and trading on margin, and you should be aware of your level of experience.
Any copying, reproduction, republication, as well as on the Internet resources of any materials from this website is possible only upon written permission.
The information on this website does not constitute investment advice, a recommendation, or a solicitation to engage in any investment activity.